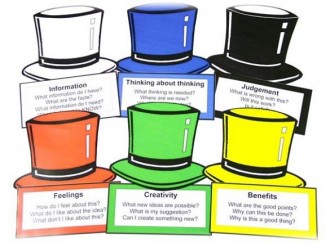
This tool was created by Edward de Bono in his book '6 Thinking Hats'.
Many successful people think from a very rational, positive viewpoint. This is part of the reason that they are successful. Often, though, they may fail to look at a problem from an emotional, intuitive, creative or negative viewpoint. This can mean that they underestimate resistance to plans, fail to make creative leaps and do not make essential contingency plans.
Similarly, pessimists may be excessively defensive, and more emotional people may fail to look at decisions calmly and rationally.
If you look at a problem with the 'Six Thinking Hats' technique, then you will solve it using all approaches. Your decisions and plans will mix ambition, skill in execution, public sensitivity, creativity and good contingency planning.
You can use Six Thinking Hats in meetings or on your own.
In meetings it has the benefit of blocking the confrontations that happen when people with different thinking styles discuss the same problem.
Each 'Thinking Hat' is a different style of thinking and provides a means for groups to plan thinking processes in a detailed and cohesive way, and in doing so to think together more effectively.
The premise of the method is that the human brain thinks in a number of distinct ways which can be deliberately challenged, and hence planned for use in a structured way allowing one to develop tactics for thinking about particular issues. De Bono identifies six distinct directions in which the brain can be challenged. In each of these directions the brain will identify and bring into conscious thought certain aspects of issues being considered (e.g. gut instinct, pessimistic judgement, neutral facts). None of these directions are completely natural ways of thinking, but rather how some of us already represent the results of our thinking.
Coloured hats are used as metaphors for each direction. Switching to a direction is symbolized by the act of putting on a coloured hat, either literally or metaphorically. These metaphors allow for a more complete and elaborate segregation of the thinking directions. The six thinking hats indicate problems and solutions about an idea the thinker may come up with.
Since the hats do not represent natural modes of thinking, each hat must be used for a limited time only. Also, many will feel that using the hats is unnatural, uncomfortable or even counter productive and against their better judgement.
This is how it works:
With this thinking hat you focus on the data available. Look at the information you have, and see what you can learn from it. Look for gaps in your knowledge, and either try to fill them or take account of them.
This is where you analyze past trends, and try to extrapolate from historical data.
'Wearing' the red hat, you look at problems using intuition, gut reaction, and emotion. Also try to think how other people will react emotionally. Try to understand the responses of people who do not fully know your reasoning.
Using black hat thinking, look at all the bad points of the decision. Look at it cautiously and defensively. Try to see why it might not work. This is important because it highlights the weak points in a plan. It allows you to eliminate them, alter them, or prepare contingency plans to counter them.
Black Hat thinking helps to make your plans 'tougher' and more resilient. It can also help you to spot fatal flaws and risks before you embark on a course of action. Black Hat thinking is one of the real benefits of this technique, as many successful people get so used to thinking positively that often they cannot see problems in advance. This leaves them under-prepared for difficulties.
The yellow hat helps you to think positively. It is the optimistic viewpoint that helps you to see all the benefits of the decision and the value in it. Yellow Hat thinking helps you to keep going when everything looks gloomy and difficult.
The Green Hat stands for creativity. This is where you can develop creative solutions to a problem. It is a freewheeling way of thinking, in which there is little criticism of ideas. A whole range of creativity tools can help you here.
The Blue Hat stands for process control. This is the hat worn by people chairing meetings. When running into difficulties because ideas are running dry, they may direct activity into Green Hat thinking. When contingency plans are needed, they will ask for Black Hat thinking, etc.
